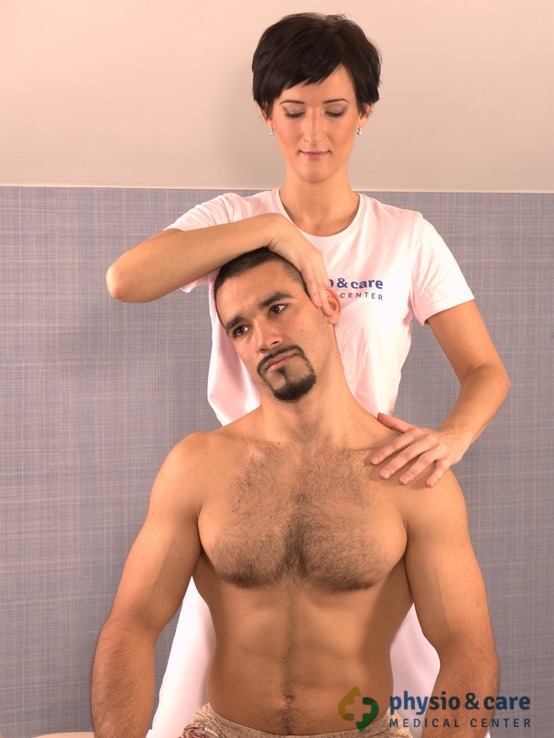
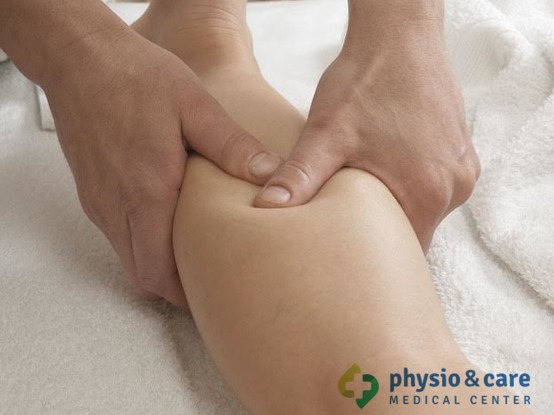
Mobilization techniques
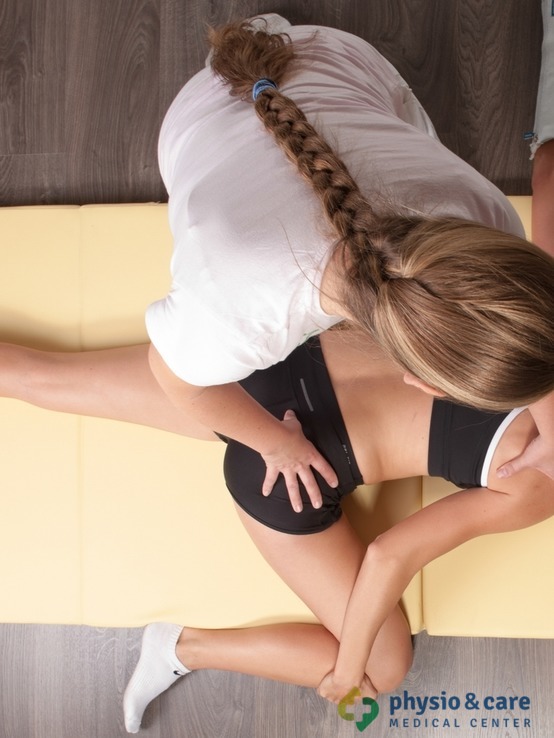
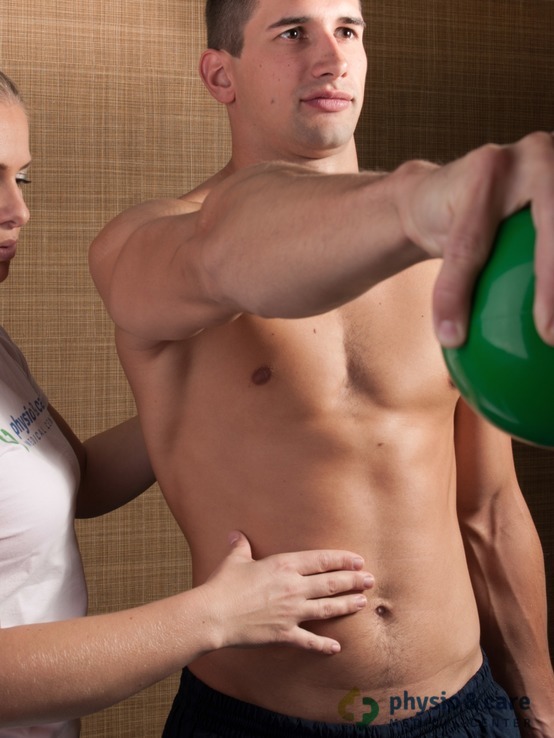
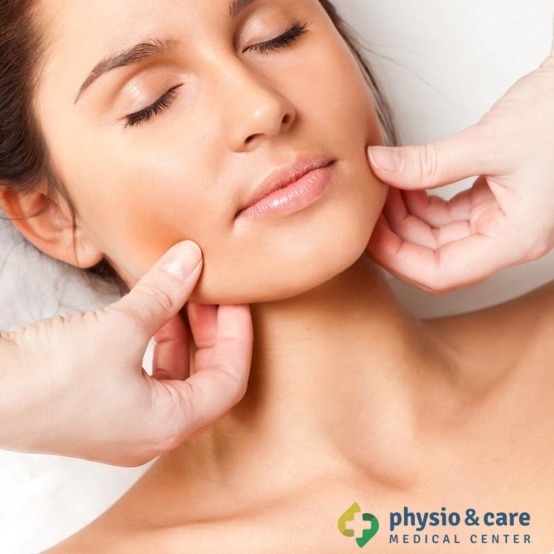
Mobilization techniques are used for the recovery of joint mobility in a specific malfunction. Mobilization techniques remove functional blockades of musculoskeletal system resulting from various causes. The objective is to remove restrictions of movement and create the best conditions for gradual recovery of the impaired function. Mobilization of joints ranks among the most important components in the release of the affected joints. It is an essential part in restoring full functional range of motion.
Mobilization can be carried out at all joints of the body. Mobilization is the method often used in re-education of the impaired locomotive activity. It is performed by physiotherapists without patient’s help, so it can also be called a passive method.